What Is The Endocannabinoid System?

What Is The Endocannabinoid System In Humans?
As part of the body’s overall control and equilibrium, the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) serves as an important regulatory and balancing mechanism.
There is evidence that the ECS is a possible therapeutic target for a wide range of physiological diseases, including:
- appetite stimulation
- blood pressure
- embryonic development
- blood pressure
- embryonic development
- energy balance
- immune response
- memory and learning
- nausea and vomiting control
- pain
How Does The Endocannabinoid System Work?
Although additional research is needed to acquire a better grasp of the endocannabinoid system, experts know it consists of three major components:
Endocannabinoids
Endocannabinoids, sometimes termed endogenous cannabinoids, are molecules similar to cannabinoids but are generated by the human body.
Experts have identified two primary endocannabinoids thus far:
- anandamide (AEA)
- 2-arachidonoylglyerol (2-AG)
These aid with the smooth operation of internal processes. Because your body makes them when it needs them, it is hard to say what the average level of each is.
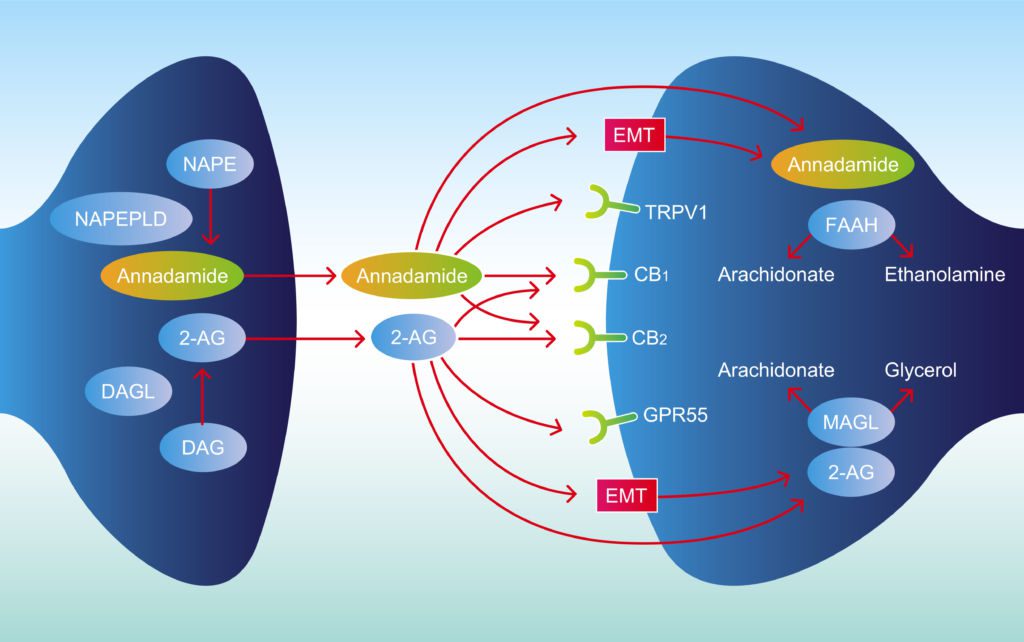
Endocannabinoid Receptors
Endocannabinoid receptors are receptors found all over your body. Endocannabinoids attach to these receptors to tell the ECS to go and function.
In the human body, there are two primary endocannabinoid receptors:
- CB1 Receptors: primarily located in the Central Nervous System
- CB2 Receptors: primarily located in the Peripheral Nervous System
Endocannabinoids are capable of binding to either receptor. The effects depend on the location of the receptor and the endocannabinoid to which it binds.
Enzymes
Enzymes are crucial for breaking endocannabinoids after they have served their purpose.
Two primary enzymes are responsible for this:
- fatty acid amide hydrolase: breaks down AEA
- monoacylglycerol acid lipase: breaks down 2-AG
Therapeutic Uses Of Cannabinoids
According to recent studies, multiple promising therapeutic targets have gotten identified in the ECS. The body can synthesize endocannabinoids; however, the Cannabis sativa plant also contains various cannabinoids that have medical use in research.
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and Cannabidiol (CBD) are two of the most well-known cannabinoids (CBD). They can also bind to cannabinoid receptors and generate effects comparable to endocannabinoid compounds. Mainly, THC is the cannabinoid responsible for creating the “high” that many people associate with cannabis, but CBD does not.
According to further studies, cannabinoids may be useful in treating a wide range of ailments, including multiple sclerosis-related muscle tension, nausea, vomiting, and sleep difficulties linked with chemotherapy.
Conclusion
Although not everything about the endocannabinoid system is currently understood, research suggests it is an essential component in the body’s efforts to preserve equilibrium and perform its functions appropriately.
For information on CBD, check out the following article:
